Rolling bearing knowledge that cannot be ignored
Popularity:Publication time:2025-03-15
Basic concepts of rolling bearings
Rolling bearings are widely used important mechanical components, widely applied in various fields of national economy and defense. In the national economy, it is known as the "joint of industry", and in the national defense industry, it is an essential military material. In terms of technical status, bearing steel is the steel type with the most demanding and strict technical indicators among various alloy steels.
The basic structure of a rolling bearing
Rolling bearings are widely used as basic components in various types of machinery. Rolling bearings are generally composed of four basic geometric parts: inner ring, outer ring, rolling elements, and cage (commonly known as the "four major components", and in most practical work environments, lubricants are also required). Due to the significant impact of lubricating grease on the performance of bearings, bearings are also known as five major components including lubricating grease.

In thrust bearings, the ring that matches the shaft is called the shaft ring, and the ring that matches the bearing seat or mechanical component shell is called the seat ring. Basic structure
Inner ring
The inner ring is usually assembled on the shaft and rotates together with the shaft.
Outer Ring
The outer ring is usually installed in the bearing seat or mechanical component housing to provide support. However, in some applications, there may also be outer ring rotation, inner ring fixation, or both inner and outer rings rotating.
rolling element
The rolling elements roll between the inner and outer rings, and the surface on the ring that allows the rolling elements to roll is called a raceway. The raceway of a ball bearing is also called a groove. Its types include ball, cylindrical roller, needle roller, tapered roller, and spherical roller, etc. The size and number of rolling elements directly affect the bearing capacity of the bearing.
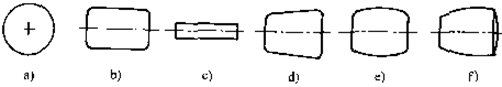
a)球 b)圆柱滚子 c)滚针 d)圆锥滚子
e)对称型球面滚子 f)非对称型球面滚子
Holder
The cage evenly separates a set of rolling elements in the bearing, guiding them to move on the correct track and improving the load distribution and lubrication performance inside the bearing.

Stamped steel plate holder:
1. Wave shaped retaining frame; 2. Riveted cage for deep groove ball bearings; 3. Retainers for self-aligning roller bearings;
Brass solid holder:
4. Riveted solid cage for deep groove ball bearings; 5-angle contact ball bearing brass solid retainer; 6-cylinder roller bearings with riveted brass solid retention; Fiberglass reinforced nylon cage:
7-row angular contact ball bearing solid cage; 8. Solid cage for cylindrical roller bearings;
轴承行业在生产过程中:
Main dimensions of two rolling bearings
The main dimensions of rolling bearings determine the boundary of the bearing, the dimensions that represent its contour, and the important dimensions for installing the bearing onto the shaft or housing. There are mainly bearing inner diameter d, bearing outer diameter D, bearing width (height) B (H), complete bearing width T, chamfer size r, etc. For internal dimensions, they belong to design dimensions and are not specified in principle.
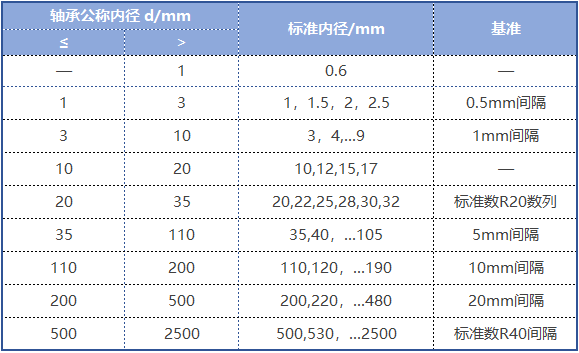
The inner diameter (d) of metric bearings specifies 90 standard sizes within the range of 0.6-2500mm, as shown in the table below:
标 准 内 径
Tolerance grade of three rolling bearings
Bearing tolerance grade refers to a specific combination of different external dimensional tolerances, positional tolerances, and rotational accuracy, which are expressed using certain methods. At present, bearings in China adopt ISO tolerance grades, with the code "P" indicating it.
Radial bearing tolerance grade
The tolerance grades of radial bearings (excluding tapered roller bearings) are divided into five levels, namely 0, 6, 5, 4, and 2, and their accuracy increases in sequence.
Tolerance grade of tapered roller bearings
The tolerance level of tapered roller bearings is divided into five levels, namely 0, 6 (6x), 5, 4, and 2, and their accuracy increases in sequence.
Thrust bearing tolerance
The tolerance level of thrust bearings is divided into four levels, namely 0, 6, 5, and 4, and their accuracy increases in sequence.
The tolerance levels of bearing related parts include
Steel balls are divided into eleven levels: 3, 5, 10, 16, 20, 24, 28, 40, 60, 100, and 200, with precision ranging from high to low.
Needle rollers are divided into three levels: 2, 3, and 5, with precision ranging from high to low.
Cylindrical rollers and tapered rollers are divided into grades 0, I, II, and III, with precision ranging from high to low.
The external dimensional tolerance of a bearing refers to the deviation of the inner diameter, outer diameter, width (height), and chamfer size of the bearing ring.
The dimensional deviation of rolling bearings is specified according to the tolerance level of the bearing, based on the type and size of the bearing.
The tolerance of the inner and outer diameter dimensions of the bearing does not comply with the GB/T 1800 tolerance and fit series basic standards, and the inner hole has a negative tolerance.
There are two main tolerance standards for rolling bearings, namely GB/T 307.1 "Tolerances for radial bearings of rolling bearings" and GB/T 307.4 "Tolerances for thrust bearings of rolling bearings".
The proportional relationship between the tolerance levels of radial bearings: